Introduction to the Three-Axis CNC Machining Process
What is a three-axis machining method?
Three-axis milling technology originated from traditional rotary file machining and has been further developed on its basis. It is a process that performs milling on the X-axis and Y-axis. In three-axis machining, the workpiece remains fixed while the tool moves along three axes to mill the part. It is suitable for automated and interactive operations such as milling slots, drilling, and cutting sharp edges. Since three-axis machining is performed only on three axes, its process is relatively simple and can remove material from different directions such as front, back, left, right, and up and down. Although three-axis machining is one of the most basic technologies, it is more than enough to meet basic machining needs depending on the production scale and workpiece requirements.

Three-axis CNC machining is a basic machining method in which the tool moves along the three axes of X, Y, and Z. This machining method is suitable for simple planes and three-dimensional shapes. The tool moves along the X, Y, and Z axes to trim excess material on the part. Three-axis CNC machining generally refers to variable speed linear motion in three different directions, such as left and right, up and down, and front and back. In three-axis CNC machining, only one surface can be machined at a time, so it is particularly suitable for the machining of disc-type parts. Although this machining method is relatively simple, it can already meet the requirements for some basic machining needs.
The advantage of three-axis CNC machining is that it is relatively low cost and is very suitable for processing simple geometric shapes. For beginners or small workshops, three-axis CNC machining is an ideal entry choice. However, for more complex geometric shapes and high-precision machining requirements, three-axis CNC machining may be difficult to handle, and then you need to consider four-axis or five-axis CNC machining.
Overall, the three-axis CNC machining process is a basic but very practical technology that is suitable for many common machining tasks, especially in the production of parts that do not require highly complex shapes or high precision requirements.
Application of three-axis machining methods
Three-axis machining methods have been widely used in the manufacturing industry. It can be used to manufacture various machine tool parts, precision molds, die-casting molds, ship accessories, and automotive parts. In addition, three-axis machining technology also has important applications in the medical industry, aerospace industry, and electronics industry.
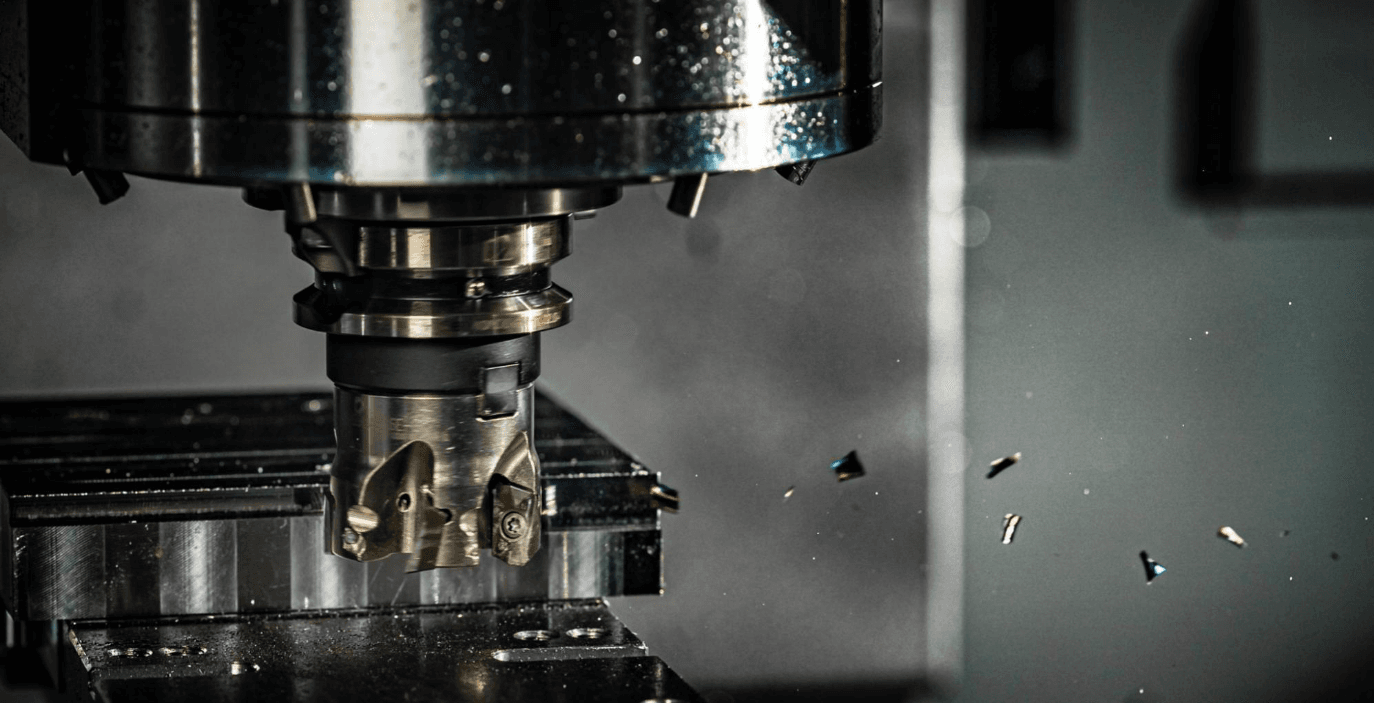

Advantages and Disadvantages of Three-axis Machining
The main advantages of three-axis machining include high efficiency, low cost, simple structure, high machining accuracy, and fewer machining tools required. At the same time, three-axis machining also has the advantages of a high degree of automation, good quality stability, and simple operation.
However, the three-axis machining method also has certain limitations, mainly due to the size, geometry, and complexity of the parts, and cannot be processed in all directions.
Application of three-axis machining method in actual production
In actual production, the three-axis machining method can be flexibly adjusted according to different workpiece requirements. Different machining processes can be selected for different workpiece shapes and machining requirements to achieve the best machining effect and economic benefits. For example, when it is necessary to process complex surface shapes, a ball head cutter can be used to use three-axis machining to perform precision machining on the curved surface.
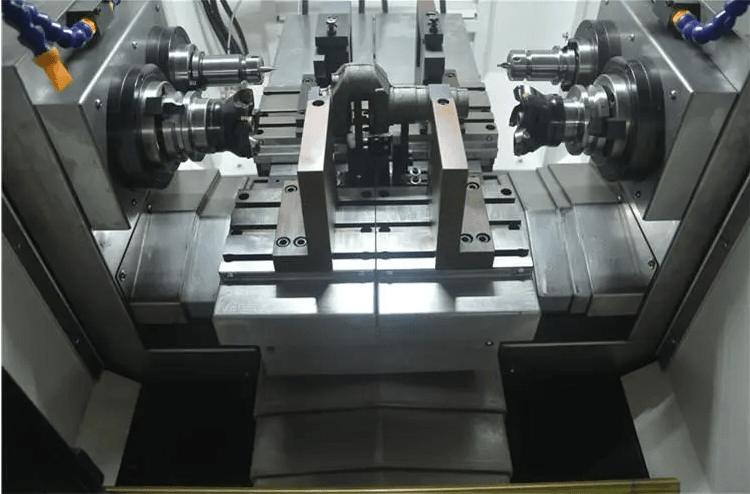
In summary, the three-axis machining method is a simple, efficient, and economical CNC machining technology, which is widely used in the manufacturing industry. For the production of parts that require high-precision machining, the three-axis machining method is still an indispensable process choice.
